How logging system Bootstrapped in Spring Boot Application
Summary Following diagram demonstrated the process to bootstrap and use Logback for loggings in Spring Boot applciation.
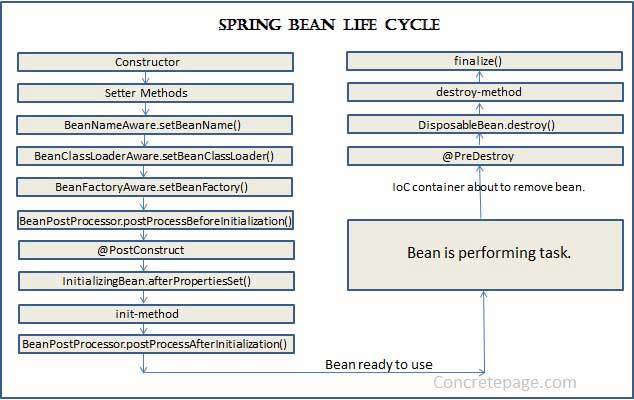 A bean life cycle includes the following steps.
A bean life cycle includes the following steps.
Spring framework provides following 4 ways for controlling life cycle events of bean:
The org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean interface specifies a single method −
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
The org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean interface specifies a single method −
void destroy() throws Exception;
The default init and destroy methods in bean configuration file can be defined in two ways:
Bean local definition applicable to a single bean Global definition applicable to all beans defined in beans context
Local definition is given as below.
<beans>
<bean id="demoBean" class="com.howtodoinjava.task.DemoBean"
init-method="customInit"
destroy-method="customDestroy"></bean>
</beans>
Where as global definition is given as below. These methods will be invoked for all bean definitions given under
<beans default-init-method="customInit" default-destroy-method="customDestroy">
<bean id="demoBean" class="com.howtodoinjava.task.DemoBean"></bean>
</beans>
Spring 2.5 onwards, you can use annotations also for specifying life cycle methods using @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy annotations.
@PostConstruct annotated method will be invoked after the bean has been constructed using default constructor and just before it’s instance is returned to requesting object. @PreDestroy annotated method is called just before the bean is about be destroyed inside bean container. A sample implementation will look like this:
package com.howtodoinjava.task;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class DemoBean
{
@PostConstruct
public void customInit()
{
System.out.println("Method customInit() invoked...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void customDestroy()
{
System.out.println("Method customDestroy() invoked...");
}
}
execution(* concert.Performance.perform()) and !bean('woodstock')
@Aspect
public class Audience {
@Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
public void silenceCellPhones() {
Before performance
Fortunately, there’s a way: the @Pointcut annotation defines a reusable pointcut within an @AspectJ aspect. The next listing shows the Audience aspect, updated to use @Pointcut.
@Aspect
public class Audience {
@Pointcut("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
public void performance() {} //Define named pointcut
@Before("performance()")
public void silenceCellPhones() {
System.out.println("Silencing cell phones");
@Before("performance()")
public void takeSeats() {
System.out.println("Taking seats");
}
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; public class Audience {
public void watchPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) { try {
System.out.println("Silencing cell phones"); System.out.println("Taking seats");
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="audience">
<aop:pointcut
id="performance"
expression="execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))" />
<aop:around Declare around advice
pointcut-ref="performance" method="watchPerformance"/> </aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
to use AspectJ’s @DeclareParents annota¬tion to magically introduce a new method into an advised bean. But AOP introduc¬tions aren’t exclusive to AspectJ. Using the
package com.springinaction.knights.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.springinaction.knights.BraveKnight; import com.springinaction.knights.Knight; import com.springinaction.knights.Quest; import com.springinaction.knights.SlayDragonQuest;
@Configuration
public class KnightConfig {
@Bean
public Knight knight() {
return new BraveKnight(quest());
}
@Bean
public Quest quest() {
return new SlayDragonQuest(System.out);
}
}
In a Spring application, an application context loads bean definitions and wires them together. The Spring application context is fully responsible for the creation of and wiring of the objects that make up the application. Spring comes with several imple¬mentations of its application context, each primarily differing only in how it loads its configuration.
When the beans in knights.xml are declared in an XML file, an appropriate choice for application context might be ClassPathXmlApplicationContext.1
These system services are commonly referred to as cross-cut¬ting concerns because they tend to cut across multiple components in a system.
Your components are littered with code that isn’t aligned with their core func¬tionality. A method that adds an entry to an address book should only be con¬cerned with how to add the address and not with whether it’s secure or transactional.
Although it’s possible to work with Spring using either bean factories or applica¬tion contexts, bean factories are often too low-level for most applications. Therefore, application contexts are preferred over bean factories. We’ll focus on working with application contexts and not spend any more time talking about bean factories.
As you can see, a bean factory performs several setup steps before a bean is ready to use. Let’s break down figure 1.5 in more detail: 1 Spring instantiates the bean. 2 Spring injects values and bean references into the bean’s properties. 3 If the bean implements BeanNameAware, Spring passes the bean’s ID to the set-BeanName() method. 4 If the bean implements BeanFactoryAware, Spring calls the setBeanFactory() method, passing in the bean factory itself. 5 If the bean implements ApplicationContextAware, Spring calls the set-ApplicationContext() method, passing in a reference to the enclosing appli¬cation context. 6 If the bean implements the BeanPostProcessor interface, Spring calls its post- ProcessBeforeInitialization() method. 7 If the bean implements the InitializingBean interface, Spring calls its after- PropertiesSet() method. Similarly, if the bean was declared with an init-method, then the specified initialization method is called. 8 If the bean implements BeanPostProcessor, Spring calls its postProcess-AfterInitialization() method. 9 At this point, the bean is ready to be used by the application and remains in the application context until the application context is destroyed. 10 If the bean implements the DisposableBean interface, Spring calls its destroy() method. Likewise, if the bean was declared with a destroy-method, the specified method is called.
· Spring began to support Servlet 3.0, including the ability to declare servlets and filters in Java-based configuration instead of web.xml. · You should now have a good idea of what Spring brings to the table. Spring aims to make enterprise Java development easier and to promote loosely coupled code. Vital to this are dependency injection and aspect-oriented programming. When it comes to expressing a bean wiring specification, Spring is incredibly flexible, offering three primary wiring mechanisms: · Explicit configuration in XML · Explicit configuration in Java · Implicit bean discovery and automatic wiring · in many cases, the choice is largely a matter of personal taste, and you’re welcome to choose the approach that feels best for you. Spring attacks automatic wiring from two angles: · Component scanning—Spring automatically discovers beans to be created in the application context. · Autowiring—Spring automatically satisfies bean dependencies. Working together, component scanning and autowiring are a powerful force and can help keep explicit configuration to a minimum.
package soundsystem;
public interface CompactDisc { void play();
}
package soundsystem;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SgtPeppers implements CompactDisc {
private String title = "Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band"; private String artist = "The Beatles";
public void play() {
System.out.println("Playing " + title + " by " + artist);
}
}
package soundsystem;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration @ComponentScan
public class CDPlayerConfig {
}
</html>
- The _eventId_ portion of the button’s name is a clue to Spring Web Flow that what follows is an event that should be fired. When the form is submitted by clicking that button, a phoneEntered event is fired, triggering a transition to lookupCustomer.
Flow execution key
```xml
<p>The address is outside of our delivery area. You may
still place the order, but you will need to pick it up
yourself.</p>
<![CDATA[
<a href="${flowExecutionUrl}&_eventId=accept">
Continue, I'll pick up the order</a> |
<a href="${flowExecutionUrl}&_eventId=cancel">Never mind</a>
11>
Note that the customerReady end state includes an
States, transitions, and entire flows can be secured in Spring Web Flow by using the
As configured here, access to the view state will be restricted to only users who are granted ROLE_ADMIN access (per the attributes attribute). The attributes attribute takes a comma-separated list of authorities that the user must have to gain access to the state, transition, or flow.
Spring uses HttpMessageConverters to render @ResponseBody (or responses from @RestController).
If a bean you add is of a type that would have been included by default anyway (such as MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter for JSON conversions), it replaces the default value. A convenience bean of type HttpMessageConverters is provided and is always available if you use the default MVC configuration. It has some useful methods to access the default and user-enhanced message converters (For example, it can be useful if you want to manually inject them into a custom RestTemplate).
On the contrary, REST has little to do with RPC. Whereas RPC is service oriented and focused on actions and verbs, REST is resource oriented, emphasizing the things and nouns that comprise an application.
Put more succinctly, REST is about transferring the state of resources—in a representational form that is most appropriate for the client or server—from a server to a client (or vice versa).
It’s a small start, but you’ll build on this controller throughout this chapter as you learn the ins and outs of Spring’s REST programming model.
Representation is an important facet of REST. It’s how a client and a server communicate about a resource. Any given resource can be represented in virtually any form. If the consumer of the resource prefers JSON, then the resource can be
Meanwhile, a human user viewing the resource in a web browser will likely prefer seeing it in HTML (or possibly PDF, Excel, or some other human-readable form). The resource doesn’t change—only how it’s represented.
Understanding how ContentNegotiatingViewResolverworks involves getting to know the content-negotiation two-step:
Determine the requested media type(s).
Find the best view for the requested media type(s).
The @ResponseBodyannotation tells Spring that you want to send the returned object as a resource to the client, converted into some representational form that the client can accept. More specifically, DispatcherServletconsiders the request’s Acceptheader and looks for a message converter that can give the client the representation it wants.
Just as @ResponseBody tells Spring to employ a message converter when sending data to a client, the @RequestBody tells Spring to find a message converter to convert a resource representation coming from a client into an object. For example, suppose that you need a way for a client to submit a new Spittle to be saved. You can write the controller method to handle such a request like this:
The body of the POST request is expected to carry a resource representation for a Spittle. Because the Spittleparameter is annotated with @RequestBody, Spring will look at the Content-Type header of the request and try to find a message converter that can convert the request body into a Spittle.
For example, if the client sent the Spittle data in a JSON representation, then the Content-Type header might be set to application/json. In that case, DispatcherServletwill look for a message converter that can convert JSON into Java objects. If the Jackson 2 library is on the classpath, then MappingJackson2Http-MessageConverterwill get the job and will convert the JSON representation into a Spittle that’s passed into the saveSpittle()method. The method is also annotated with @ResponseBodyso that the returned Spittle will be converted into a resource representation to be returned to the client.
Notice that the @RequestMappinghas a consumesattribute set to application/json. The consumesattribute works much like the producesattribute, only with regard to the request’s Content-Typeheader. This tells Spring that this method will only handle POSTrequests to /spittles if the request’s Content-Typeheader is application/json. Otherwise, it will be up to some other method (if a suitable one exists) to handle the request.
The key thing to notice in listing 16.3is what’s not in the code. Neither of the handler methods are annotated with @ResponseBody. But because the controller is annotated with @RestController, the objects returned from those methods will still go through message conversion to produce a resource representation for the client.The @ExceptionHandler annotation can be applied to controller methods to handle specific exceptions. Here, it’s indicating that if a SpittleNotFoundException is thrown from any of the handler methods in the same controller, the spittleNotFound() method should be called to handle that exception.
@ExceptionHandler(SpittleNotFoundException.class)@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)public @ResponseBody Error spittleNotFound(SpittleNotFoundException e) { long spittleId = e.getSpittleId(); return new Error(4, “Spittle [” + spittleId + “] not found”);}
@ExceptionHandler(SpittleNotFoundException.class) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND) public @ResponseBody Error spittleNotFound(SpittleNotFoundException e) { long spittleId = e.getSpittleId(); return new Error(4, “Spittle [” + spittleId + “] not found”); }
Because spittleNotFound() always returns an Error, the only reason to keep Response-Entity around is so you can set the status code. But by annotating spittleNotFound() with @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND), you can achieve the same effect and get rid of ResponseEntity.
Again, if the controller class is annotated with @RestController, you can remove the @ResponseBody annotation and clean up the code a little more:
@ExceptionHandler(SpittleNotFoundException.class) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND) public Error spittleNotFound(SpittleNotFoundException e) { long spittleId = e.getSpittleId(); return new Error(4, “Spittle [” + spittleId + “] not found”); }
public Spittle fetchSpittle(long id) {
RestTemplate rest = new RestTemplate();
ResponseEntity
"http://localhost:8080/spittr-api/spittles/{id}",
Spittle.class, id); if(response.getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.NOT_MODIFIED) { throw new NotModifiedException(); } return response.getBody(); }
Just like the getForEntity() method, postForEntity() returns a Response-Entity
By passing in HttpMethod.GET as the HTTP verb, you’re asking exchange() to send a GET request. The third argument is for sending a resource on the request, but because this is a GET request, it can be null. The next argument indicates that you want the response converted into a Spitter object. An
Used this way, the exchange() method is virtually identical to the previously used getForEntity(). But unlike getForEntity()—or getForObject()—exchange() lets you set headers on the request sent. Instead of passing null to exchange(), you pass in an HttpEntity created with the request headers you want.
RESTful architecture uses web standards to integrate applications, keeping the interactions simple and natural. Resources in a system are identified by URLs, manipulated with HTTP methods, and represented in one or more forms suitable for the client.
Spring’s philosophy of avoiding checked exceptions, you don’t want to let the JMSException escape this method, so you’ll catch it instead.
In the catch block, you can use the convertJmsAccessException() method from Spring’s JmsUtils class to convert the checked JMSException to an unchecked JmsException. This is effectively the same thing JmsTemplate does for you in other cases.
A message-listener container is a special bean that watches a JMS destination, waiting for a message to arrive. Once a message arrives, the bean retrieves the message and passes it on to any message listeners that are interested.
JmsInvokerServiceExporter is much like those other service exporters. In fact, note that there’s some symmetry in the names of JmsInvokerServiceExporter and HttpInvokerServiceExporter. If HttpInvokerServiceExporter exports services that communicate over HTTP, then JmsInvokerServiceExporter must export services that converse over JMS.
As it turns out, AMQP offers several advantages over JMS. First, AMQP defines a wire-level protocol for messaging, whereas JMS defines an API specification. JMS’s API specification ensures that all JMS implementations can be used through a common API but doesn’t mandate that messages sent by one JMS implementation can be consumed by a different JMS implementation. AMQP’s wire-level protocol, on the other hand, specifies the format that messages will take when en route between the producer and consumer. Consequently, AMQP is more interoperable than JMS—not only across different AMQP implementations, but also across languages and platforms.
In JMS, there are just three primary participants: the message producer, the message consumer(s), and a channel (either a queue or a topic) to carry the message between producers and consumers. These essentials of the JMS messaging model are illustrated in figures 17.3 and 17.4.
In JMS, the channel helps to decouple the producer from the consumer, but both are still coupled to the channel. A producer publishes messages to a specific queue or topic, and the consumer receives those message from a specific queue or topic. The channel has the double duty of relaying messages and determining how those messages will be routed; queues route using a point-to-point algorithm, and topics route in publish/subscribe fashion.
In contrast, AMQP producers don’t publish directly to a queue. Instead, AMQP introduces a new level of indirection between the producer and any queues that will carry the message: the exchange. This relationship is illustrated in figure 17.8.
Figure 17.8. In AMQP, message producers are decoupled from message queues by an exchange that handles message routing.
For example, to have a message routed to multiple queues with no regard for the routing key, you can configure a fanout exchange and several queues like this:
Summary Following diagram demonstrated the process to bootstrap and use Logback for loggings in Spring Boot applciation.
Symptoms When you are using integrated authentication (Kerberos connection) for MS SqlServer connection, there is one possible error :
Why to extract resources from jar to local disk
Normal approach to debug maven
How to watch specific kubenetes deployment by labels
Background It’s typical to get various network connection issues when you run commands within corporation network. For example, you’ll find diversed issues w...
More developer friendly Threa Sleep
Summary As you know, staff and your safety is paramount. So what if emergency take place, such as fire in office, how to help yourself and your colleagues by...
Summary As you know, there are various event will be sent (multicast) when a specific story taken place.
IT-Solutions-For-Remote-Learning.md
IT-Solutions-For-Remote-Learning.md
IT-Solutions-For-Remote-Learning.md
Summary To talk to K8s for getting data, there are few approaches. While K8s’ official Java library is the most widely used one. This blog will look into thi...
Summary In windows operation system, if you want to get your CPU name, core, 64bit and speed in command line. Just follow below actions:
Summary Whitelabel Error Page is the default error page in Spring Boot web app. It provide a more user-friently error page whenever there are any issues when...
Summary I found a weird problem of the app Google Maps of my Oppo Android phone. That’s when you search a place in Google map, say “Central Park”, ideally th...
A debt security represents a debt owed by the issuer to an investor. Here, the investor acts as a lender to the issuer which may be a government, organisatio...
S3 download URL As you know, AWS S3 object can be downloaded/processed by S3 download URL. I’m showing you two examples on how to process S3 Object by NIO f...
What happened to a debug job hanging in IntelliJ (IDEAS) IDE? You may find when you try to debug a class in Intellij but it stuck there and never proceed, e....
Difference with Scala Kotlin takes the best of Java and Scala, the response times are similar as working with Java natively, which is a considerable advantag...
Shortcuts & tips
此文是作者英文原文的翻译文章,英文原文在:http://todzhang.com/posts/2018-06-10-jvm-warm-up/
Shortcuts for Slack
Gradle build stuck, keep on running but never ending
Key points of Reactive Programming
Frame in Swift
Argument Matching & Answers For example, you have mocked DOC with call(arg: Int): Intfunction. You want to return 1 if argument is greater than 5 and -1 ...
Dockers Concepts
How to decode path parameters in All REST WebServices calls
Linux Curl command
The concept of join points as matched by pointcut expressions is central to AOP, and Spring uses the AspectJ pointcut expression language by default.
As a general rule it should be possible to use the name as a pivot. Dimensions allow a particular named metric to be sliced to drill down and reason about th...
Shortcuts & tips
Here are some tips and notes about how to resolve algorithm issues listed in LeetCode Rotation problem
# Pigeonhole principle
你就会发现只要涉及递归的问题,都是 树的问题。
How to make thread-safe
A Facial Recognition utility in a dozen of python LOC (Lines Of Code)
What’s TLS TLS (Transport Layer Security) and its predecessor, SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), are security protocols designed to secure the communication betwee...
Java Deep Notes
Why JVM need warm up I don’t know how and why you get to this blog. But I know the key words in your mind are “warm” for JVM. As the name “warm up” suggested...
This is the second half about Java Concurrent of my blog
This blog is about noteworthy pivot points about Java Concurrent Framework Back to Java old days there were wait()/notify() which is error prone, while fr...
Algorithm Leetcode
Feelings is the language of the soul. If you want to know what’s true for you about something, look to how your’re feeling about.
Enable Kafka listener annotated endpoints that are created under the covers by a AbstractListenerContainerFactory. To be used on Configuration classes as fol...
Footprint
Why Terraform
Kafka
FX Spot is not covered by the regulation, as it is not considered to be a financial instrument by ESMA, the European Union (EU) regulator. As FX is considere...
currency pairs Direct ccy: means USD is part of currency pair Cross ccy: means ccy wihtout USD, so except NDF, the deal will be split to legs, both with...
nano seconds
Simple Binary Encoding (SBE)
“Cannot connect to remote desktop” with Citrix Receiver
A new type of Juice Put simply, Guice alleviates the need for factories and the use of new in your Java code. Think of Guice’s @Inject as the new new. You wi...
Key points All YAML files (regardless of their association with Ansible or not) can optionally begin with — and end with …. This is part of the YAML format a...
multithreading
Feature
What are protocol buffers?
Sudo in a Nutshell Sudo (su “do”) allows a system administrator to give certain users (or groups of users) the ability to run some (or all) commands as root...
ZK Motto the motto “ZooKeeper: Because Coordinating Distributed Systems is a Zoo.”
WHAT IS PRESTO?
Overview
Acceptance testing vs unit test It’s sometimes said that unit tests ensure you build the thing right, whereas acceptance tests ensure you build the right thi...
Scala String
philosophy The actor model adopts the philosophy that everything is an actor. This is similar to the everything is an object philosophy used by some object-o...
FileUtil.class
Camel’s message model In Camel, there are two abstractions for modeling messages, both of which we’ll cover in this section. org.apache.camel.Message—The ...
Settings
Exporting your beans to JMX The core class in Spring’s JMX framework is the MBeanExporter. This class is responsible for taking your Spring beans and registe...
Solace PubSub+ It is a message broker that lets you establish event-driven interactions between applications and microservices across hybrid cloud environmen...
Annotation retention policy What is Retention policy in java annotations?
App deployment, configuration management and orchestration - all from one system. Ansible is powerful IT automation that you can learn quickly.
Ansible: What Is It Good For? Ansible is often described as a configuration management tool, and is typically mentioned in the same breath as Chef, Puppet, a...
How Flexbox works — explained with big, colorful, animated gifs
commands:
Single Writer principle
KDB However kdb+ evaluates expressions right-to-left. There are no precedence rules. The reason commonly given for this behaviour is that it is a much simple...
Foreign Exchange markets
Better to use smart wait
Key concept In Scrum, a team is cross functional, meaning everyone is needed to take a feature from idea to implementation.
:100:DevOps Model Defined
https://stormforger.com/blog/2016/07/08/types-of-performance-testing/
Error of ‘ECONNRESET’ You may face error ECONNRESET from intranet, even appropriate proxy tools (e.g. cntlm) is running. The errors may looks like ```bash $ ...
Release & Testing Strategy There are various methods for safely releasing changes to Production. Each team must select what is appropriate for their own ...
Here is the typical erros log:
commands to read files var lineReader = require(‘readline’).createInterface({ input: require(‘fs’).createReadStream(‘C:\dev\node\input\git_reset_files.tx...
https://blog.leanstack.com/minimum-viable-product-mvp-7e280b0b9418
What is difference between declarations, providers and import in NgModule
Cross-Origin Request Sharing - CORS (A.K.A. Cross-Domain AJAX request) is an issue that most web developers might encounter, according to Same-Origin-Policy,...
Why @Effects? In a simple ngrx/store project without ngrx/effects there is really no good place to put your async calls. Suppose a user clicks on a button or...
View A view is also a responder (UIView is a subclass of UIResponder). This means that a view is subject to user interactions, such as taps and swipes. Thus,...
openshift vs openstack The shoft and direct answer is `OpenShift Origin can run on top of OpenStack. They are complementary projects that work well together....
Concepts Cloud computing is the on-demand demand delivery of compute database storage applications and other IT resources through a cloud services platform v...
whats @Effects You can almost think of your Effects as special kinds of reducer functions that are meant to be a place for you to put your async calls in suc...
The second advantage to a lazy subscription is that the observable doesn’t hold onto data by default. In the previous example, each event generated by the in...
Lettable operators RxJS 5.5, piping all the things
code E503 code E503 when run npm install packages, e.g.
The Docker project was responsible for popularizing container development in Linux systems. The original project defined a command and service (both named do...
The drawback of using Promises is that they’re unable to handle data sources that produce more than one value, like mouse movements or sequences of bytes in ...
Commands bible
Async Await keywords Async Await Support in TypeScript Async - Await has been supported by TypeScript since version 1.7. Asynchronous functions are prefixed ...
How Page Value is calculated
interface RandomAccess Marker interface used by List implementations to indicate that they support fast (generally constant time) random access. The primary ...
Secure FTP SFTP over FTP is the equivalant of HTTPS over HTTP, the security version
Setup WebSphere profiles and application in command line
After establishing a SSH session, you can install a default web server by executing sudo yum install httpd -y. To start the web server, type sudo service htt...
ORA-12899: Value Too Large for Column
Spring Bean Life Cycle Callback Methods
This is talking about Java JIT (Just-In-Time) compiler
Java Security well-behaved: programs should be prevent from consuming too much system resources
Noteworthy points about SeriableVersionUID in Java
s<-read.csv("C:/Users/xxx/dev/R/IRS/SHH_SCHISHG.csv") # aggregate s2<-table(s$Original.CP) s3<-as.data.frame(s2) # extract by Frequency ordered s3...
SFTP versus FTPS SS: Secure Shell An increasing number of our customers are looking to move away from standard FTP for transferring data, so we are ofte...
How do I remove a plug-in? Run Help > About Eclipse > Installation Details, select the software you no longer want and click Uninstall. (On Macintosh i...
Class loading subsystem
Maven philosophy “It is important to note that in the pom.xml file you specify the what and not the how. The pom.xml file can also serve as a documentatio...
Notes JDK 1.0 introduced rudimentary I/O facilities for accessing the file system (to create a directory, remove a file, or perform another task), accessi...
Net Protocols
SOA SOA is a set of design principles for building a suite of interoperable, flexible and reusable services based architecture. top-down and bottom-up a...
This page is about key points about Algorithm
Concept
What is the difference between Serializable and Externalizable in Java? In earlier version of Java, reflection was very slow, and so serializaing large ob...
What is NavigableMap
Concepts If you implement Comparable interface and override compareTo() method it must be consistent with equals() method i.e. for equal object by equals(...
Difference between equals and deepEquals of Arrays in Java Arrays.equals() method does not compare recursively if an array contains another array on oth...
Hashmap in JDK Some note worth points about hashmap Lookup process Step# 1: Quickly determine the bucket number in which this element may resid...
This blog is listing key new features introduced in Java 8
What is the difference between arbitrage and hedging?
Shortcuts Expand/collapse method body in code editor Cmd + +/- to expand and collapse a method body Show java doc Ctrl+J: To show JavaDoc
Enum Misc
verbose:gc verbose:gc prints right after each gc collection and prints details about each generation memory details. Here is blog on how to read verbose gc
contract of hashCode : Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during an execution of a Java application, the hashCode method must consis...
Apache
Dependency Injection Angular doesn’t automatically know how you want to create instances of your services or the injector to create your service. You must co...
ThreadLocalRandom, SecureRandm, java.util.Random, java.math.Random
JDK Versions JDK 1.5 in 2005 JDK 1.6 in 2006 JDK 1.7 in 2011 JDK 1.8 in 2014 Sun之前风光无限,但是在2010年1月27号被Oracle收购。 在被Oracle收购后对外承诺要回到每2年一个realse的节奏。但是20...
用10几行代码自己写个人脸识别程序
Eslastic Search
JSON lines
Python Scraphy
引言 有句话说有人的地方就有江湖,同样,有江湖的地方就有恩怨。在软件行业历史长河(虽然相对于其他行业来说,软件行业的历史实在太短了,但是确是充满了智慧的碰撞也是十分的精彩)中有一些恩怨情愁,分分合合的小故事,比如类似的有,从一套代码发展出来后面由于合同到期就分道扬镳,然后各自发展成独门产品的Sybase DB和微...
Hyperledger Fabric for Mortals
使用Solidity创建以太坊(Ethereum)智能合约(Smart Contract)
Reference Sublime Scope Naming Syntax Guide
大家都知道,在软件测试特别是在单元测试时,必用的一个功能就是“断言”(Assert),可能有些人觉得不就一个Assert语句,没啥花头,也有很多人用起来也是懵懵懂懂,认为只要是Assert开头的方法,拿过来就用。一个偶然的机会跟人聊到此功能,觉得还是有必要在此整理一下如何使用以及对“断言”的理解。希望可以帮助大家...
Shortcuts
深入浅出区块链系统:第一章. what you should know about blockchain
Kubernetes 和Docker Swarm 可能是使用最广泛的工具,用于在集群环境中部署容器。但是这两个工具还是有很大的差别。
在开发设计中有一些常用原则或者潜规则,根据笔者的经验,这里稍微总结一下最最常用的,以飨读者。
how to show full path in Finder window Open and run following command in terminal window defaults write com.apple.finder _FXShowPosixPathInTitle -bool true; ...
RFC origion http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec9.html#sec9.1.2)
The stark difference among Spark and Storm. Although both are claimed to process the streaming data in real time. But Spark processes it as micro-batches; wh...
可以想像一下,之前的传统应用系统,像是一个大办公室里面,有各个部门,销售部,采购部,财务部。办一件事情效率比较高。但是也有一些弊端,首先,各部门都在一个房间里。
What’s it Returns an unmodifiable view of the specified set. This method allows modules to provide users with “read-only” access to internal sets. Query ope...
What’s Kibana kibana is an open source data visualization plugin for Elasticsearch. It provides visualization capabilities on top of the content indexed on...
What’s Kibana kibana is an open source data visualization plugin for Elasticsearch. It provides visualization capabilities on top of the content indexed on...
Design philosophies
UI HTML5, AngularJS, BootStrap, REST API, JSON Backend Hadoop core (HDFS), Hive, HBase, MapReduce, Oozie, Pig, Solr
Purpose of BA 带来一些商业价值(收益) 解决业务痛点
REST API must be hypertext driver Roy’s interview
Binary Tree A binary tree is a tree in which no node can have more than two children. A property of a binary tree that is sometimes important is that th...
eBooks list of various books Node.js
Common solutions
Toggle crosshair
It’s annoying to keep on repeating typing same login and password when you access multiple systems within office or for systems in external Internet. There a...
Difference between mutal funds and hedge funds
Differences between not in, not exists , and left join with null
concepts
404 error for customized domain (such as godday) 404 There is not a GitHub Pages site here. Go to github master branch for gitpages site, manually add CN...
RQFII RQFII stands for Renminbi Qualified Foreign Institutional Investor. RQFII was introduced in 2011 to allow qualified foreign institutional investors to ...
hall-of-frame by commit numbers git shortlog -s | sort -n -r
includes() vs some()
Get permission denied error when sudo su (or hyphen in sudo command) bash: /home/YOURNAME/.bashrc: Permission denied That’s because you didn’t add “-“ hyphen...
Docker Errors
Concepts LVS means Linux Virtual Server, which is one Linux built-in component.
(‘—–Unexpected error:’, <type ‘exceptions.TypeError’>) datetime.datetime.now()
RAID RAID is Reductant Array Independent Disk,
Concepts
Description
How to setup Git in Mint Linux =================================================
DB sharding in YHD
Microservice Services are organized around capabilities, e.g., user interface front-end, recommendation, logistics, billing, etc. Services are small in ...
Codecache The maximum size of the code cache is set via the -XX:ReservedCodeCacheSize=N flag (where N is the default just mentioned for the particular com...
Script bible